Carbon-nanotube transistors could be used to detect minute quantities of disease biomarkers, such as the proteins implicated in prostate cancer, according to new experiments by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania in the US. The technique could rival conventional immunoassays when it comes to sensitivity, cost and speed.
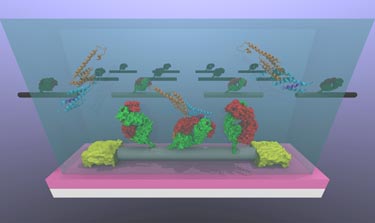
Detecting prostate cancer
Conventional techniques to detect proteins are typically based on some form of immunoassay, with the most famous of these being ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). This technique involves introducing an enzyme-modified antibody protein to an unknown amount of target molecule or protein, known as an antigen, and allowing them to bind together. Unreacted antibodies are washed away, leaving behind only antibody–antigen pairs.
The reaction can usually be detected by a colour change in the solution or by a fluorescent signal. The degree of colour change or fluorescence depends upon the number of enzyme-modified antibodies present, which in turn depends on the initial concentration of antigen in the sample.
Although such tests are routinely used in hospitals and clinics, they are quite long, taking several days or even weeks to complete. They are also costly, complicated to perform and can only detect single proteins at a time.
"Our new nanotube sensors are relatively simple compared to these ELISA tests," team member Mitchell Lerner told nanotechweb.org. "Detection occurs in just minutes, not days, and even at the laboratory scale, the cost of an array of 2000 such sensors is roughly $50 or 2.5 cents per sensor."
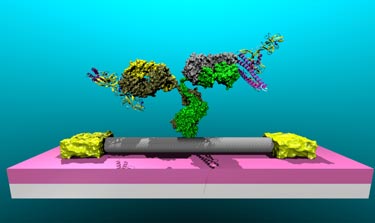
Detecting Lyme disease
More importantly still, the sensors are much more sensitive to the target proteins in question. Indeed the Pennsylvania researchers showed that they could detect a prostate-cancer biomarker called osteopontin (OPN) at 1 pg/mL, which is roughly 1000 times lower than that possible with clinical ELISA measurements.
The team, which is led by A T Charlie Johnson of Penn Department of Physics and Astronomy, made its nanotube sensors by attaching OPN-binding antibodies to carbon-nanotube transistors on a silicon chip. Many proteins in the body bind very strongly to specific target molecules or proteins, and OPN is no exception. When the chip is immersed in a test sample, the OPN binds to the antibodies, something that changes the electronic characteristics of the transistor. Measuring the voltage and current through each device thus allows the researchers to accurately measure how much OPN there is in the sample.
The technique could also be used to detect a host of other diseases by replacing the OPN-binding antibody with surface functional groups sensitive to different biomarkers, said Lerner. One biomarker that the researchers have already succeeded in detecting is that implicated in Lyme disease. They have also managed to detect salmonella bacteria using their technique.

In the lab
"Our sensors could be used as point-of-care diagnostic tools that allow doctors to obtain test results in real time for a variety of diseases," Lerner added. "And by integrating many proteins onto a single chip, we could look for hundreds of disease biomarker proteins simultaneously in a singe small-volume sample."
The team said that it is now busy improving its devices. Protein attachment chemistry is quite complex and sometimes limits how well nanotubes actually conduct current, with some devices stopping functioning altogether. "We are also trying out new sensing experiments using human serum, possibly from actual patient samples," revealed Lerner. "If these tests give good results, it would certainly be a huge step forward in taking the technology from the research lab to a hospital."
The present work is reported in three papers, which are available to read for free on the arXiv server.
About the author
Belle Dumé is contributing editor at nanotechweb.org.



